- 5 minute read
The Importance of a Secure, Recurring Payment Subscription Model
Subscription models are big business and represent an impressive and growing market segment. According to Statista, the market size of the digital subscription economy worldwide already amounted to $650 billion in 2020. The e-commerce segment is expected to reach 687 billion U.S. dollars by 2025. UBS Wealth Management and Bernstein estimate that the subscription economy will be worth $1.5 trillion by 2025, with an average annual growth rate of 18%. This would make this business one of the fastest-growing industries globally. Zuora Subscribed Institute recently published its Subscription Economy Index™(SEI) report which says that the SEI has grown 4.6x faster than the S&P 500, which stands for more traditional, product-based businesses. Software as a Service (SaaS) is still the fastest-growing sector in the index: SaaS companies in the SEI report achieved 16.2% growth in 2021 with a 19.4% compound annual growth rate (CAGR) over the last four years (2018-2021).
Subscription Models and Recurring Payments
Subscription models rely on recurring payments. The customer authorizes the merchant to charge his credit card or account automatically and at regular – weekly, monthly or annual – intervals. These recurring transactions need to be processed by specialized Payment Service Providers (PSP) that manage the entire life cycle; customer KYC/CDD, on-boarding, fraud and chargeback mitigation, payment processing and a smooth billing process. Subscription models save companies costly customer acquisition spending. Instead, Sales & Marketing must focus on a marketing strategy that guarantees a scalable revenue flow coming from existing customers. A seamless payment process is crucial to minimize the churn (subscription cancelation) rate and establish long-term customer relationships.
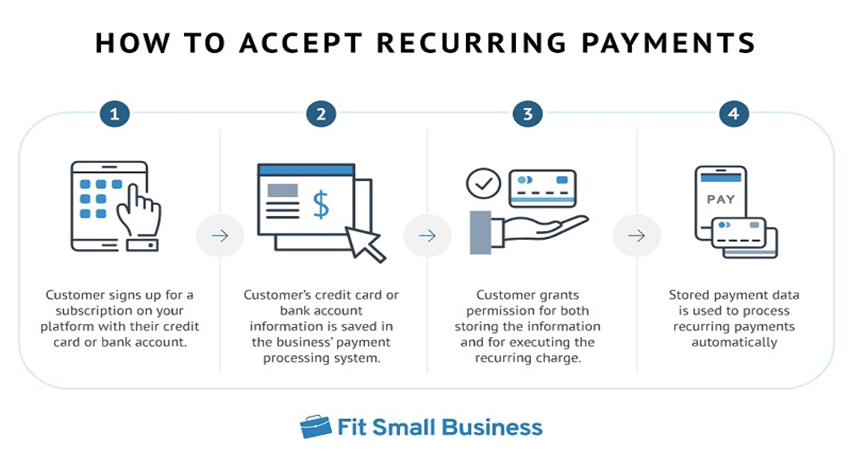
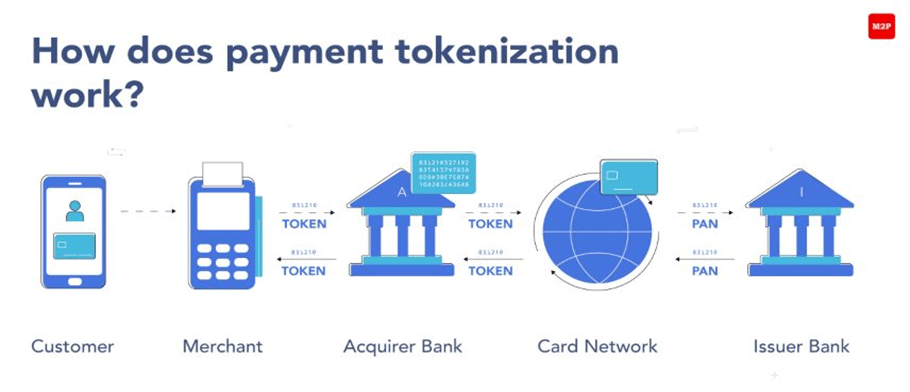
The customer authorizes a subscription-based product or service, after which the customers’ payment data is stored in the payment processor’s secure system through tokenization. Sensitive data is stored in tokens that only have value internally and are protected against fraudsters and hackers. The customer gives the merchant permission to execute the transaction periodically. The processor handles the recurring transaction through the card network. The customer will receive a confirmation once the transaction has been executed.
Streaming companies paved the way, by offering their clients subscription access to specific media (i.e., video, music, newspapers, etc.). Other industries are quickly catching up, with Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) providers clearly getting ahead of the game. According to Revenera’s 2021 Monetization Monitor Software Industry Survey, 62% of SaaS firms reported to have switched to recurring subscription revenue models over the past years and according to a recent report by SAP, 53% of all software revenue will be generated from subscriptions by the end of 2022.
Besides SaaS firms and video/media streaming companies, other industries that are profiting from the growing popularity of subscription-based payment models are:
-
- Communications: Video Conferencing, broadband networks, digital infrastructure, fiber networks.
- Manufacturers: (B2C and B2B) Brick & Mortar, supply chain, hardware products
- IoT Companies: Web-connected hardware providers
- Business Management: Legal aid, data services, market research, recruitment, advertising
Churn rates and chargebacks
Churn rates and chargebacks are subscription-based business’ worst headaches. Churn rates measure the health of a business that depends on recurring revenues. A high churn rate shows a lower customer lifetime value, which results in a reduced revenue stream. One strategy to lower churn rates is to adopt a pricing model that retains customers loyalty once the promotional period is over. Unintentional churn is yet another hurdle that subscription businesses face. Involuntary churn could be caused by insufficient funds or maxed-out credit cards or connectivity issues. This problem can be solved by dunning, the process of retrying payments attempts and reminders to customer after a transaction has been declined. Processors can set up back-up payment methods for each customer. To keep customers and minimize churn, it is crucial to optimize customers’ experience and guarantee transparency.
Merchants must offer their customers a growing variety of payment methods, including local payment methods (LPM) to expand their business into regional markets. This is especially the case when a company wants to expand cross-border. Compliance rules can get quite challenging. Regulators expect subscription revenue to be logged according to certain standards. If not effectively managed, subscription model businesses can face audits and compliance issues around revenue tracking.Therefore, it is so important to partner with a payment processor with vast experience in the various aspects of subscription-based recurring payments. A PSP that specializes in processing recurring payments can help merchants overcome the following hurdles:
- Scaling issues around recurring billing and rebilling capabilities
- Security and data protection
- Process, manage and track recurring revenue
- Meet PCI-DSS compliance requirement
- Mitigate fraud risk
- Manage high transaction volumes
- Inaccurate forecasts and reporting
- Downtime (solved by providing payment gateway stability)
- Collections issues to invoice disputes
- Minimize chargeback-to-sales ratios
- Card Updater capabilities
- Retention tools to help you keep your customers
Customers are often ‘seduced’ to buy a subscription service based a sweet offer. After the trial period ends, the customer is charged the full price, which often leads to disputes where the customer forgot about the subscription and wants to cancel after the new period has started. This causes time-consuming and costly chargebacks, which lead to financial and reputational damage. High chargebacks rates can be the result of the merchant’s marketing strategies, but it can also be caused by fraudulent customers. In this case, we speak of chargeback fraud.
How to prevent recurring billing chargebacks?
Be clear about free trial periods, offer transparent pricing models and make it easy for customers to cancel subscriptions in time. Spell out the frequency of charges, the date(s) of future transactions and the amount to be charged. Allow customers to confirm the subscription details before the transaction is processed and highlight recurring payments. Make sure that subscriptions become a win-win for both the merchants and the customer. If the customer is left to guess, with no way to contact the merchant in time, this leads to subscriptions not being canceled on time, or to double-billing or missed billing cycles. Issues that result in a recurring billing chargeback (Code 13.2 /Visa and Code 4850 /Mastercard). Increased chargeback risk that is a reason for acquiring banks and processors to label subscription business as high-risk. A sizable part of chargebacks results from “friendly fraud” where customer try to mislead the merchant. For example, the cardholder orders a “starter pack” and files a chargeback after enjoying the service/access. Card networks have implemented some restrictions to prevent recurring transaction chargebacks. Besides the 120 days from the date of the original transaction to request a chargeback, Visa updated its rules related to recurring transactions in 2020.
Merchants Must:
- Gain express consent from the customer
- Supply a copy of the terms and conditions to the cardholder at the time of subscription
- Supply more detailed transaction receipts
- Appoint the charge as a “free trial” (on the cardholder statement and other locations)
- Simplify cancellations
Conclusion
Having learned how companies can reap the benefits from smart subscription models, while addressing the challenges posed by recurring payments, the importance of partnering with a processor that is specialized in handling subscription payments cannot be overestimated. A partner that knows how to overcome the hurdles discussed in this article, while streamlining and managing incoming revenue. Cost- and time-efficient payment processing turns the perceived high-risk, attached to high-volume recurring billing, into a frictionless payment journey both for the consumer and the merchant. Subscription models have a lot to offer and – if managed intelligently – guarantee a secure and long-term customer relationship.
Let’s Grow Together
Contact Segpay Europe, the global payment processor with decades of experience in recurring payments, for more information about subscription models.




